Google Images, photo sharing sites like Flickr and social bookmarking sites like Pinterest have made it even more easy (and socially acceptable) to steal images. Most people think that if an image comes up in a Google Images search, it’s fair game.
As an artist or photographer — especially if you make a living through selling digital images — you’ll obviously want to make sure that people aren’t getting your work for free. While there is no way of stopping people from using your images entirely (short of not uploading them in the first place), you can make it more difficult or inconvenient for them. There are also ways to make sure that images are marked as belonging to you, so even if they do end up on another site, people can find their way back to the original creator.
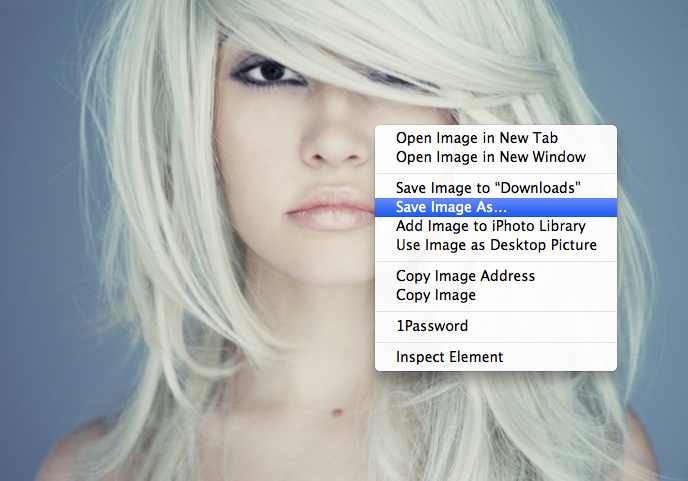
Disabling Right-Click
The easiest way to download images is by right-clicking on them and selecting “save image”. While it’s still easy enough to download images in other ways, if you disable this capability, you’ll put off less web-savvy image thieves and people who can’t be bothered with the hassle of looking at your HTML or searching the browser cache.
The easiest way to do this in WordPress is by using the No Right Click Images Plugin. This plugin uses Javascript to disable the contextual menu when you right-click on an image. It only affects right-clicking on images, so if users right-click on a link to open it in a new tab, for example, this won’t be affected. You can also choose to display a copyright message or another image when an image is right-clicked.
The main problem with this plugin is that it can be disabled by simply turning off Javascript, but most users won’t know this or won’t bother disabling it unless they really want your image in particular. It’s also possible that the Javascript could cause a conflict with some other code in the theme or a different plugin.
To protect your images fully, you’ll also need to disable the default image linking that occurs when you insert an image in WordPress. To do this just choose “none” in the “link to” dropdown box when you’re uploading your image.
Adding A Copyright Notice
Contrary to popular belief, you don’t need to put a copyright notice on your website content to protect it. Copyright is automatically owned by the creator and you only need to register copyright if you’re worried about someone claiming your work at their own at some point in the future.
Putting a copyright notice on your website is not the same as registering copyright but it can act as enough of a deterrent to prevent casual downloads and may cause people to stop and realize they’re not actually allowed to download your pictures to do with as they please.
Most WordPress themes come with an inbuilt copyright notice in the footer. If your theme doesn’t have this, you can add it easily with the following code:
Copyright ©
< ?php $the_year = date("Y"); echo $the_year; ? >
< ?php bloginfo('url'); ? >
All Rights Reserved.
This code will automatically fill in your website name and update to the current year. Just enter it into the footer.php file in your theme’s directory.
A footer copyright notice is not normally very noticeable, so you might also want to have a more prominent and detailed one. WordPress suggests putting the following text in your sidebar so it is visible at all times:
© [Full Name] and [Blog Name], [Current Year or Year Range]. Unauthorized use and/or duplication of this material without express and written permission from this blog’s author and/or owner is strictly prohibited. Excerpts and links may be used, provided that full and clear credit is given to [Your Name] and [Your Blog Name] with appropriate and specific direction to the original content.
You can also add a copyright notice directly to your images either by using an image editing program or by adding a text watermark using a plugin like Watermark Reloaded or Watermark My Image. Keep in mind the fact that if your copyright notice is in the corner of your image, it can be easily cropped out.
Watermark Your Images
Adding a textual copyright watermark may deter image downloaders but as previously mentioned, they are easily cropped out and won’t stop people who really want your images. Another solution is to use a semi-transparent image to watermark over the whole of your image.
This is easily accomplished with a plugin like our very own Watermark for Sell Media. Unlike some watermark plugins, ours doesn’t alter the original file uploaded. Instead, it watermarks only the lower resolution versions, which are displayed on your website. You can use either your signature or logo to watermark your images automatically as they are uploaded. Other solutions can be found in the WordPress plugin repository (choose one with high ratings, test carefully and delete all inactive or unused plugins).
Watermarks like this are typically extremely difficult to remove so they can be quite effective, but they are rather distracting for people looking at your photos so it’s a personal decision whether to use them or not and how large to make the watermark.
Add A DMCA Badge To Your Site
The DMCA offers free protection for your website which includes a takedown service if you find someone using your images or other content without permission. The DMCA will threaten legal action on your behalf with usually scares infringers into taking down your content right away.
Putting a DMCA badge on your site can act as a deterrent for serial image stealers and they also offer a free image watermarking service.
There is also a DMCA plugin available for WordPress that inserts the badge on all your website pages automatically.
Disable Hotlinking
Disabling hotlinking does not stop people from downloading your images, but rather it will stop them from embedding them in their own site by linking out directly to your website. This is a common practice for new bloggers who don’t realise they’re doing anything wrong.
You can prevent hotlinking by editing your .htaccess file but there are also plugins available to do the job for you. Plugins like Hotlink Protection simply stop external web servers from linking to your files, while others like ByREV WP-PICShield provide more functionality and replace the hotlinked image with a warning message or another image of your choice.
Do A Reverse Image Search
While it’s not always possible to stop people from stealing your images, in some cases they may stop using them on their website if you ask nicely. Many web users simply do not realise that it’s illegal or even bad manners to take images that they find online and if you ask them to take them down, they’ll happily comply.
You can find other sites that are using your images by using a handy trick in Google Images. You’ll need to do this individually for each image so it may not be practical to check all your images, but it’s worth checking in on from time to time.
To use this service, go to images.google.com and click the camera icon in the search box to search by image. You can either enter a URL from your website here or you can even drag in an image from your computer. Google will come back with all images that are visually similar. If you find your exact image, you can click through to the site and contact the owner.
Take Precautions But Don’t Be Obsessive
It makes sense to take a few steps to protect your images when you rely on them for your livelihood but remember that whatever measures you take, nothing will ultimately stop someone from stealing your content and photos if they really want to.
Don’t waste your time trying to achieve the impossible. It’s better to simply try and deter casual downloaders by making it more inconvenient to access your pictures.
Watermarking your images with your website address in an unobtrusive way is a decent compromise for most people. While web users lacking morals may crop it out, the majority won’t bother and this may even work get you some extra exposure and drive traffic to your site.
